Water & Energy
WATER & ENERGY
Water Quantity Impacts – Fossil Fuels Use Large Amounts of Water
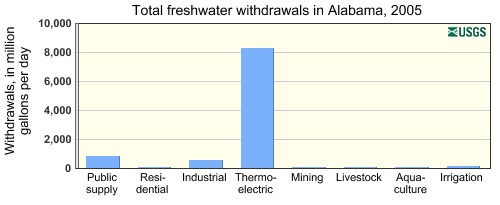
More than half of Alabama’s electricity comes from coal and nuclear power plants which are large consumers of our water.
83% of water taken out of our rivers in Alabama is used for cooling coal and nuclear power plants. While around 90% of this is returned, the volume that is lost is significant and can have major impacts during periods of drought and water shortage. Hydropower accounts for about 5% of our energy use but requires damming of rivers and the water evaporated from hydropower reservoirs is also lost from the system. From Alabama Water Use Report 2010.
Renewable energy, such as distributed solar uses virtually NO water to create electricity.
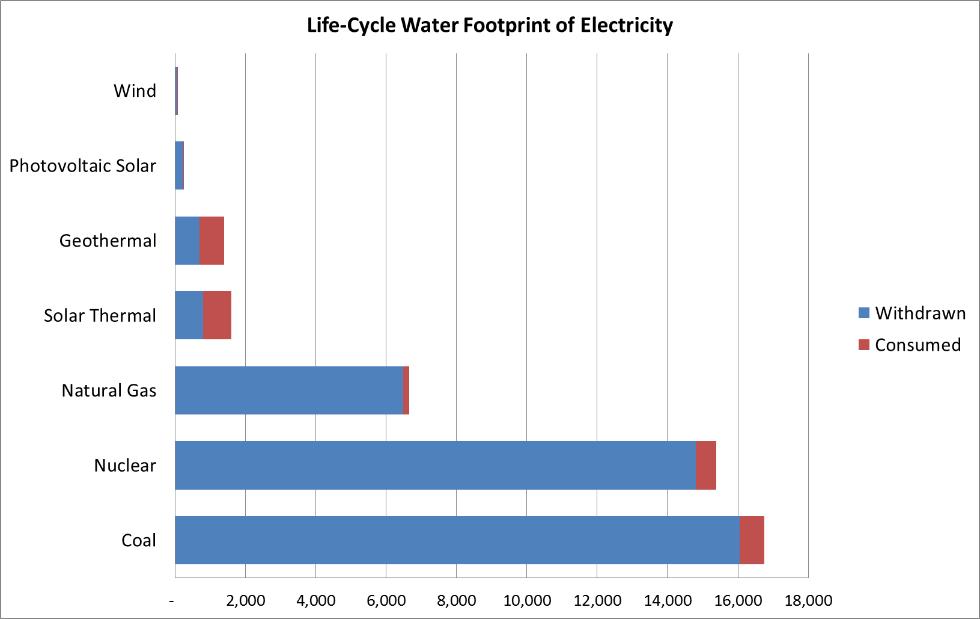
From River Network’s “Burning our Rivers”.
Water Quality Impacts of Energy in Alabama – Coal is Dirty!

Coal Extraction – Strip mining (a.k.a. surface mining) and longwall mining (a.k.a. underground mining) are the methods of choice for coal extraction in Alabama. As a result, many streams are polluted. Coal mines transform the landscape and alter streams forever. Coal mines from the past have left a dirty legacy for our generation and future generations to clean up. These old coal mines were not properly reclaimed, resulting in hundreds of acid mine drainage (AMD) sites. AMD sites pollute streams with heavy metals, sediment, and acids.
Coal Ash – Coal ash is the waste left over after coal is burned to generate power. Coal ash contains arsenic, lead, mercury, chromium, and a range of harmful heavy metals and toxic pollutants that poison the air and drinking water supplies of communities living near coal ash dumpsites. Coal ash threatens the respiratory, cardiovascular, and neurological systems of people living near more than 1400 dump sites across the nation. Click here to read more about coal ash.
Coal Burning – Burning coal for electricity produces air emissions containing toxic pollution, such as Mercury. Mercury in the air, eventually ends up in the water and is consumed by fish. When Mercury gets in the fish, it makes it unsafe for people to eat the fish. In 2014, the Alabama Department of Public Health issued Fish Consumption Advisories for 75 water-bodies in Alabama.
WHAT YOU CAN DO TO HELP
- Saving energy saves water! Use less energy and be energy efficient in your home and at work. Click here for easy tips for anyone.
- Support Solar! Renewable energy, like solar, is much better for our rivers. It uses less water and causes less pollution. Click here to visit the Alabama Solar Knowledgebase website.
- Join organizations like the Alabama Rivers Alliance and help us advocate for clean energy that protect rivers and people.
Some of our partners working on solar, energy efficiency and other energy alternatives:
Southern Environmental Law Center

